Foot & Ankle Problems

What is Foot & Ankle Problems?
Foot and ankle problems encompass a range of conditions affecting the structures and functionality of the foot and ankle, including bones, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. These issues can arise from various causes and may lead to discomfort, pain, reduced mobility, and impaired quality of life.
Causes
- Injuries: Sprains, strains, fractures, and dislocations are common injuries affecting the foot and ankle, often caused by sports activities, accidents, or falls.
- Overuse Repetitive activities or excessive stress on the foot and ankle, such as prolonged standing or high-impact sports, can lead to overuse injuries like plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendinitis.
- Structural abnormalities: Conditions like flat feet, high arches, or abnormalities in bone structure can predispose individuals to foot and ankle problems.
- Medical conditions: Arthritis, diabetes, nerve disorders, and circulatory problems can contribute to foot and ankle issues.
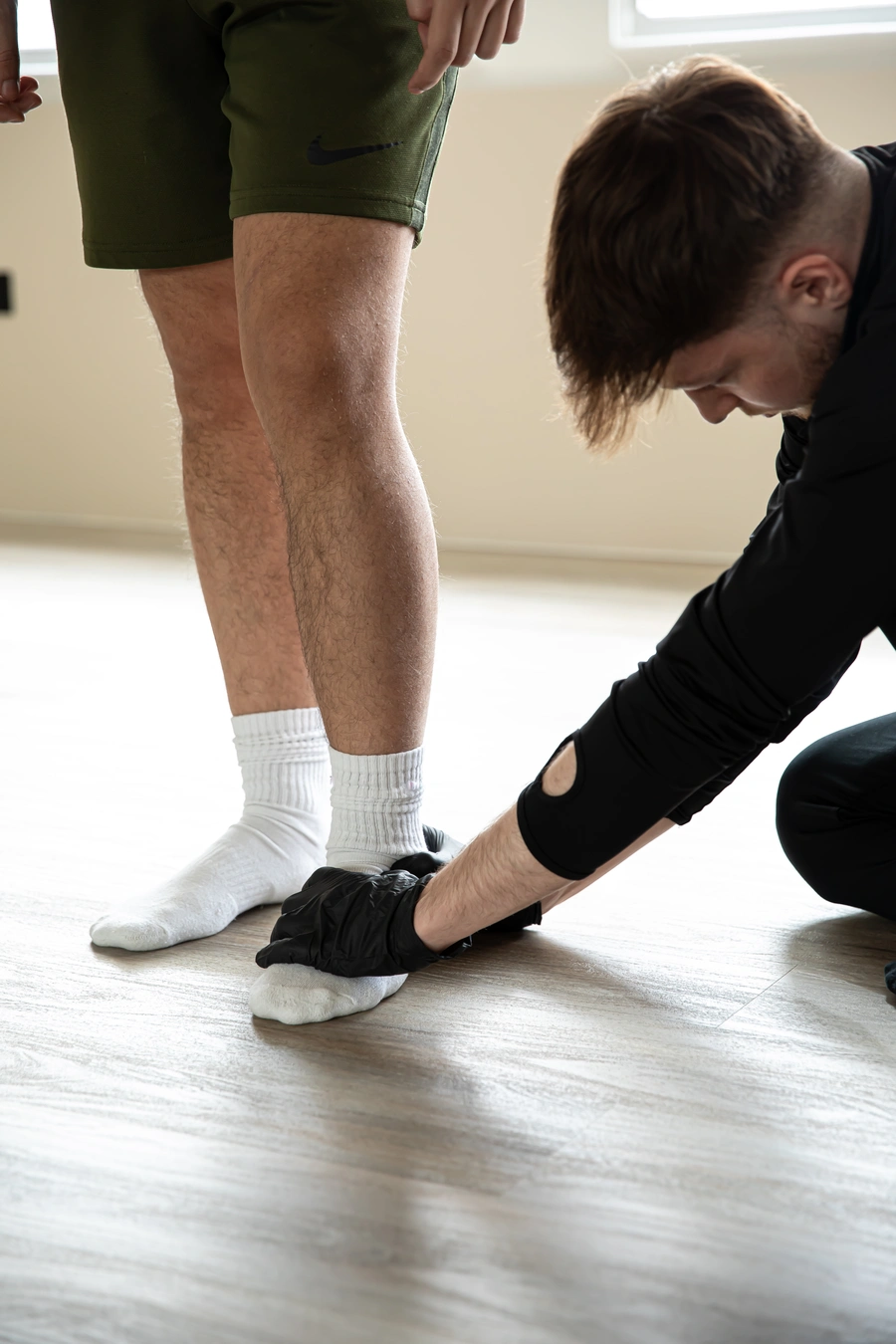
Assessment by a Physiotherapist
Physiotherapists play a crucial role in assessing and treating foot and ankle problems.
Assessment typically involves:
- History taking: Understanding the patient's symptoms, medical history, and any precipitating factors
- Physical examination Assessing range of motion, strength, flexibility, gait analysis, and conducting special tests to identify specific conditions.
- Diagnostic tests: X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, or other imaging studies may be ordered to confirm diagnosis or assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment Methods
- RICE Therapy Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation can help manage acute injuries and reduce swelling and pain
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercise programs focusing on strengthening, flexibility, and proprioception can improve stability and function.
- Orthotics: Custom-made or over-the-counter orthotic devices may be prescribed to provide support, correct alignment, and reduce strain on the foot and ankle.
- Bracing or Taping: Splints, braces, or taping techniques can offer stability and prevent further injury during physical activity.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques such as massage, joint mobilisations, and soft tissue mobilisation can alleviate pain and improve joint function.
- Modalities: Therapeutic modalities like ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or laser therapy may be used to reduce pain and promote tissue healing
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, or corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Surgery In severe cases or when conservative measures fail, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues, correct deformities, or stabilise joints.