Fractures & Dislocations
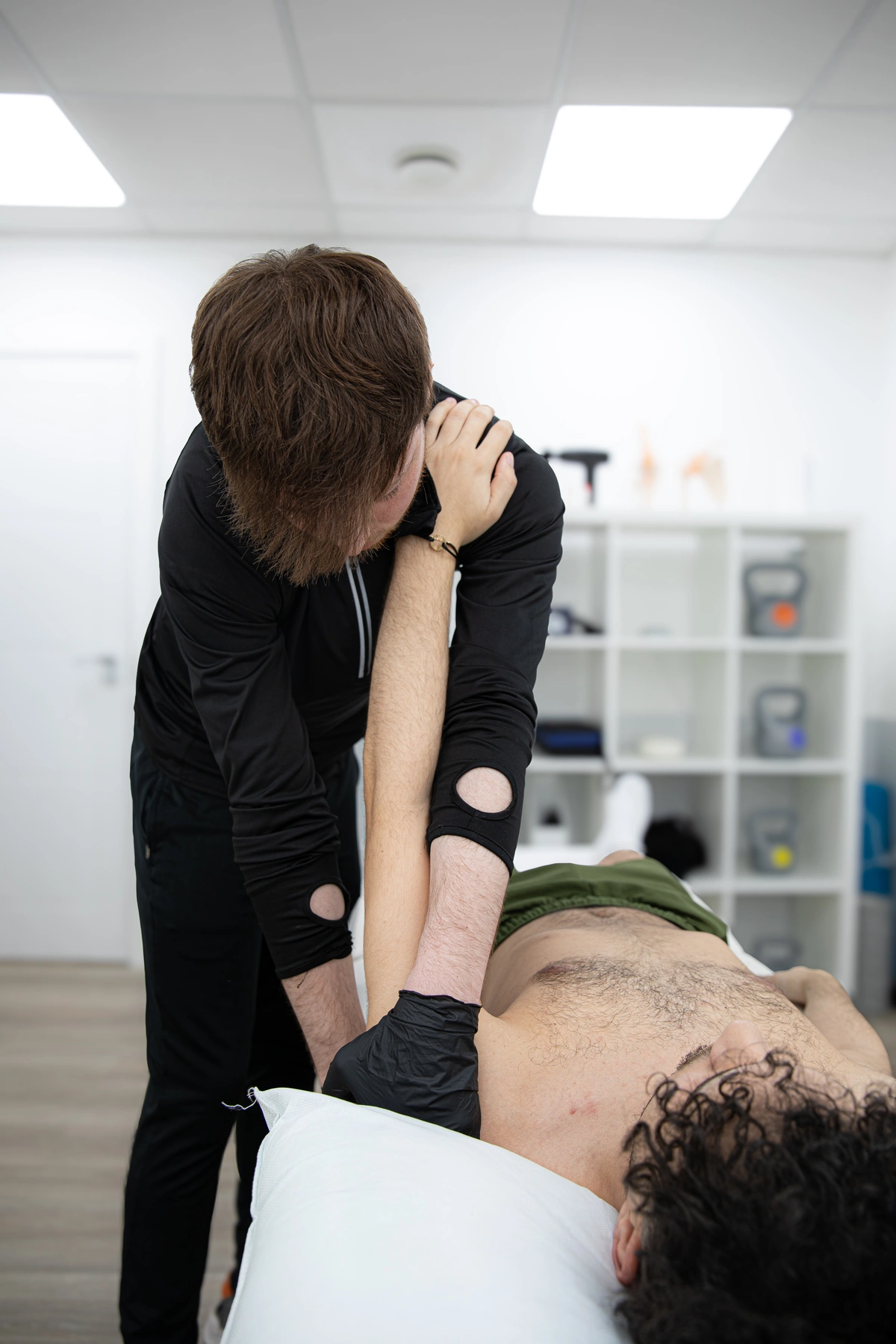
What is Fractures & Dislocations?
Fractures and dislocations are common musculoskeletal injuries that can result from various causes, such as accidents, sports injuries, or osteoporosis.
Causes
- Trauma: Fractures and dislocations often occur due to direct trauma to the bone or joint, such as falls, vehicle accidents, or impacts during sports activities
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on a bone or joint can lead to stress fractures or chronic joint instability, increasing the risk of dislocation.
- Osteoporosis: Weakening of the bones due to osteoporosis can make them more susceptible to fractures, particularly in older adults
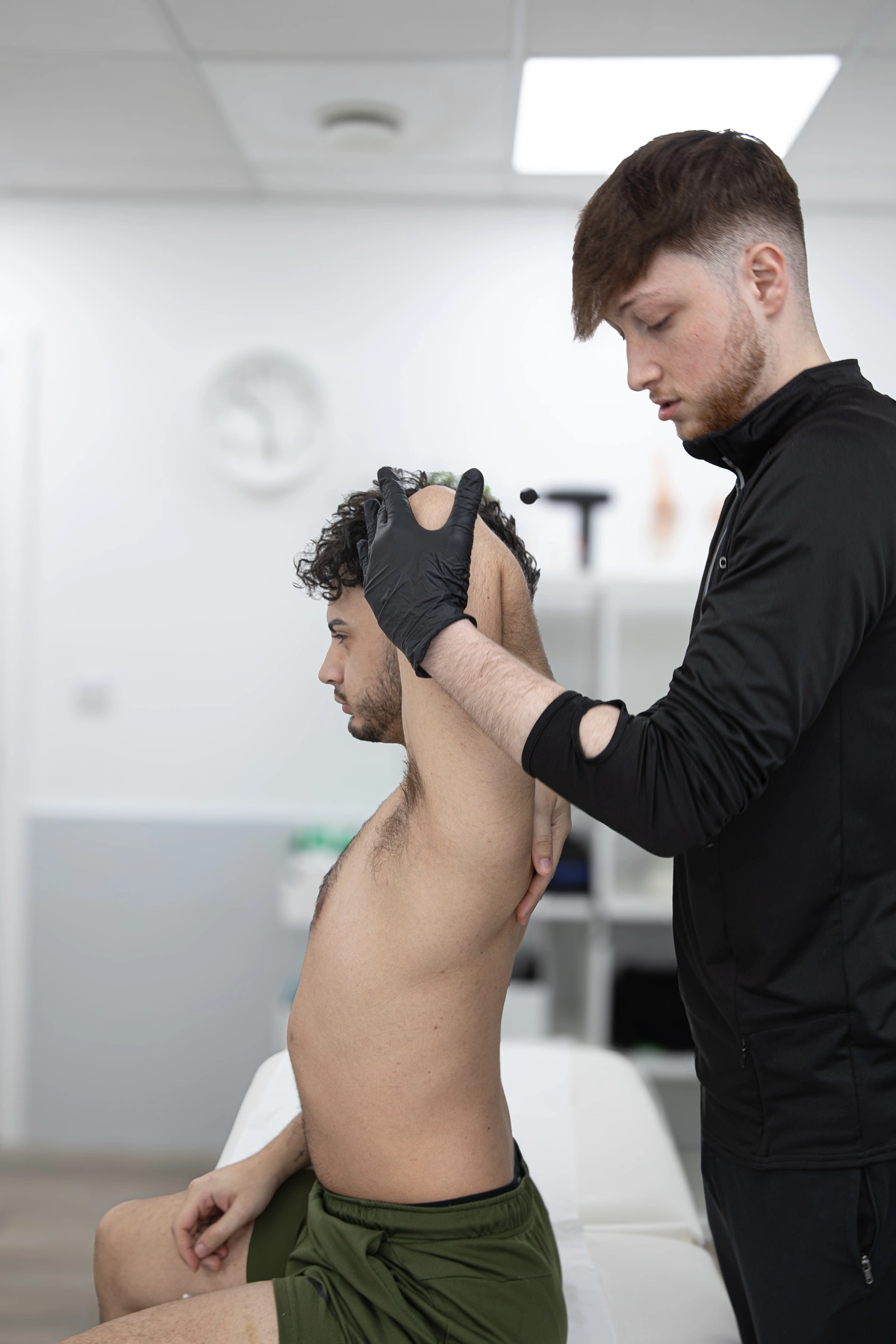

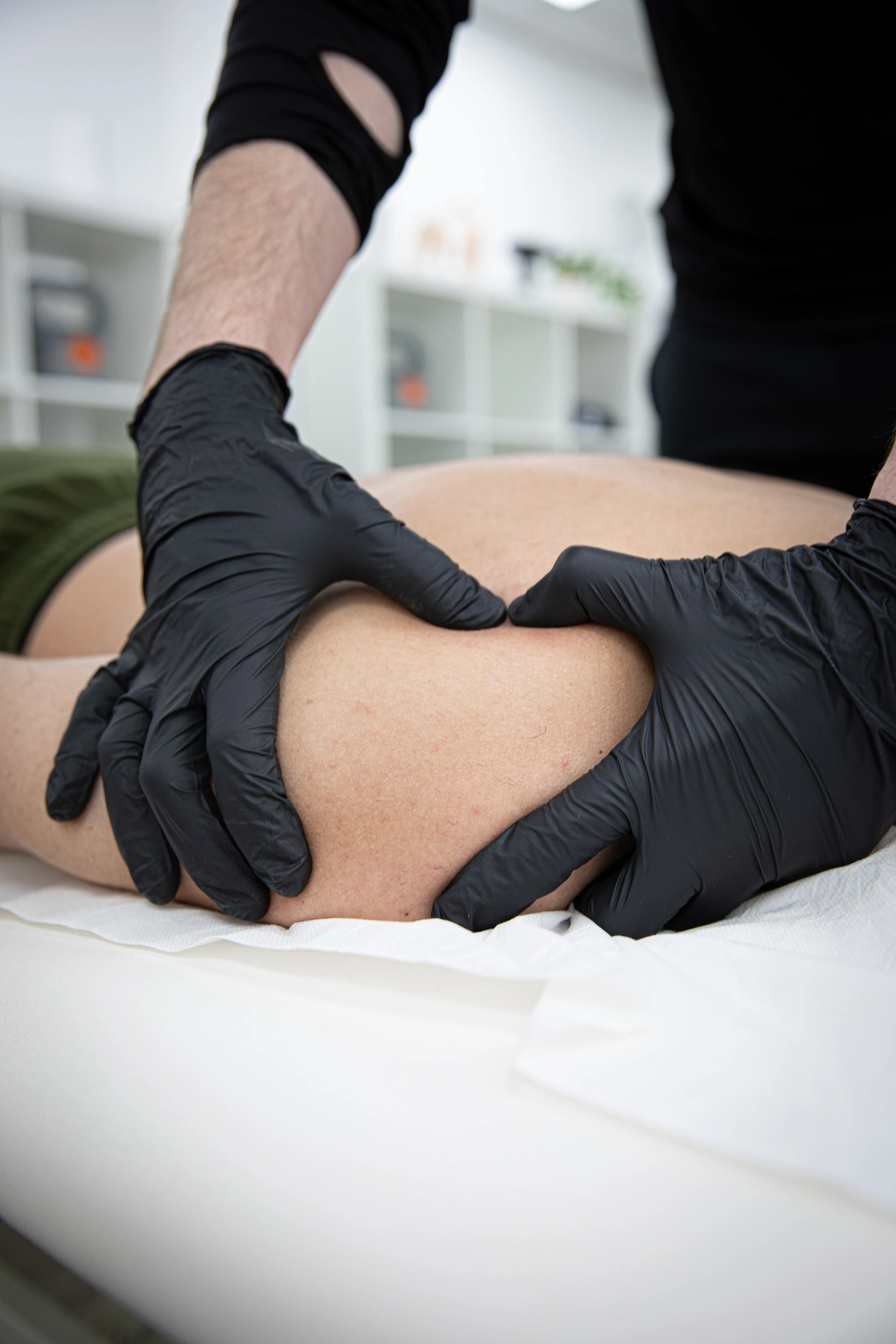
Assessment by a physiotherapist:
- History taking: The physiotherapist will gather information about the patient's symptoms, the mechanism of injury, and any previous medical history relevant to the current condition.
- Physical examination: This involves assessing the affected area for signs of swelling. deformity, tenderness, and restricted range of motion. Special tests may also be performed to evaluate joint stability and neurovascular status.
- Diagnostic tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the injury.
Treatment methods
- Immobilisation: Fractures and dislocations often require immobilisation to allow proper healing. This may involve the use of casts, splints, braces, or slings to stabilise the injured area and prevent further damage.
- Reduction: In cases of dislocations or displaced fractures, the physiotherapist or medical practitioner may need to perform a reduction procedure to realign the bones or joint back into their normal position.
- Rehabilitation exercises: Once the acute phase of healing has passed, physiotherapy plays a crucial role in restoring strength, flexibility, and function to the injured area. This may involve a tailored exercise programme focusing on a range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, proprioception training, and functional activities to facilitate a safe return to normal activities.
- Manual therapy: Hands-on techniques such as mobilisations, manipulations, and soft tissue techniques may be used to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and enhance tissue healing.
- Modalities: Modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and ice or heat therapy may be utilised to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing.
Overall, the management of fractures and dislocations requires a comprehensive approach involving accurate assessment, appropriate immobilisation, and targeted rehabilitation to achieve optimal outcomes and prevent long-term complications.