Knee Pain
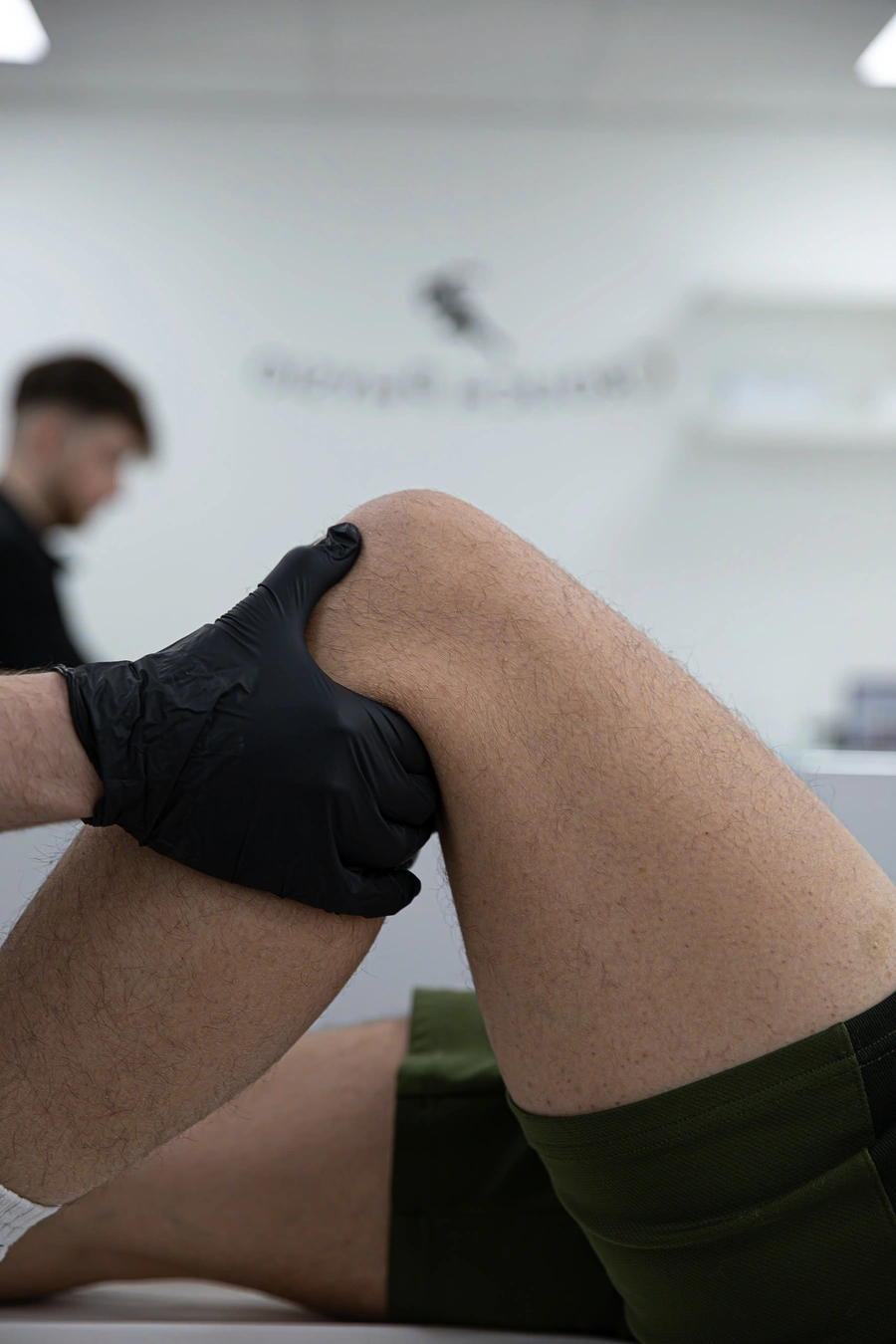
What is Knee Pain?
Knee pain is a prevalent issue that can stem from various causes, including injuries, overuse, or underlyingmedical conditions. It can affect individuals of all ages and activity levels, ranging from athletes to those with a more sedentary lifestyle. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of knee pain, encompassing patient symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment methods, from the perspective of a physiotherapist.
Symptoms/Presentation
- Pain: Patients may experience discomfort in and around the knee joint, ranging from mild to severe. This discomfort may worsen with activities like walking, running, or climbing stairs.
- Swelling: Swelling or inflammation around the knee joint is common, particularly following an injury or prolonged activity.
- Stiffness: Patients may report stiffness in the knee joint, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking in the morning.
- Instability: Some patients may feel a sensation of instability in their knee, as if it might give way. This instability can affect their balance and mobility
- Clicking or Popping: Audible or palpable clicking or popping sensations within the knee joint may occur, particularly during movement.

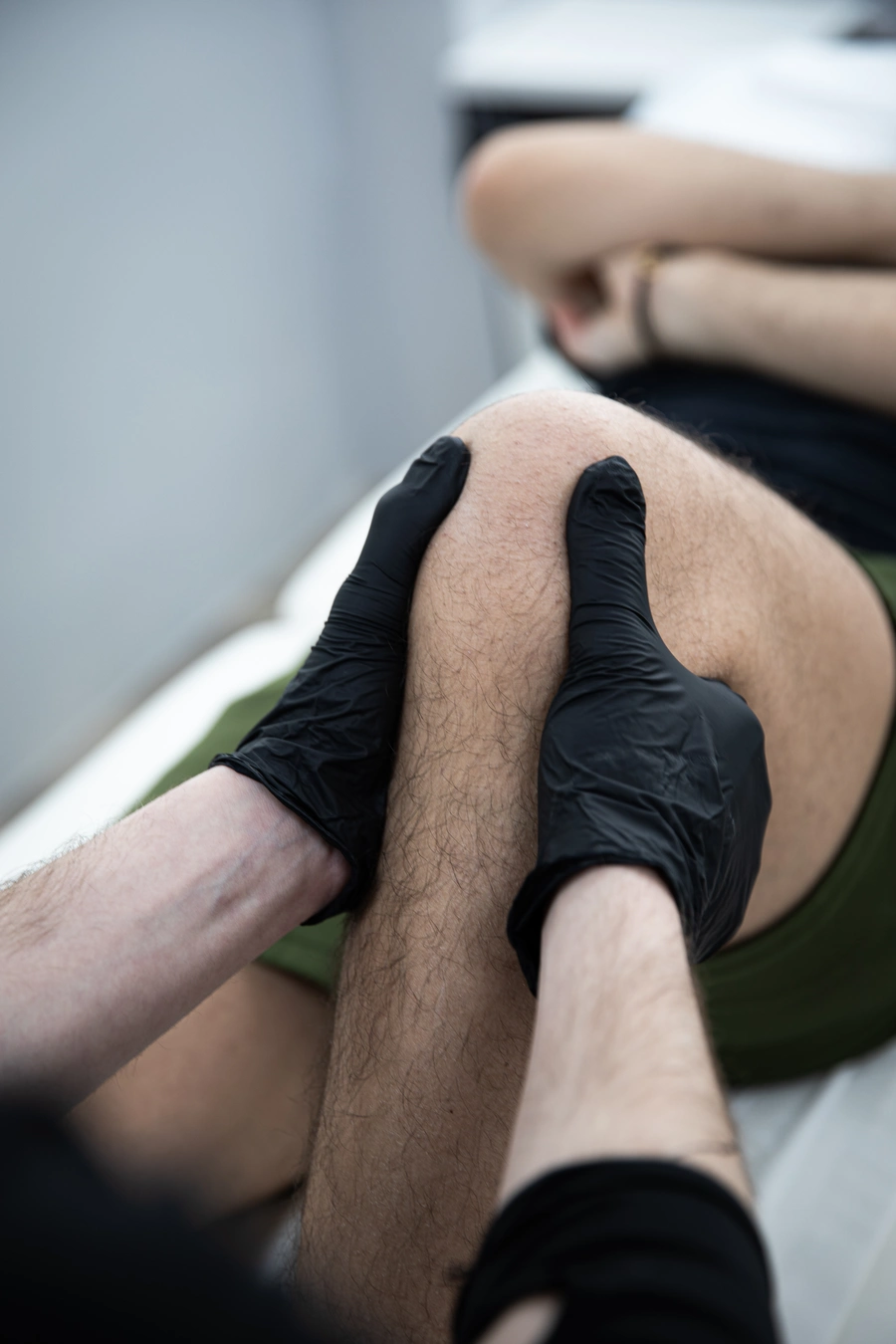
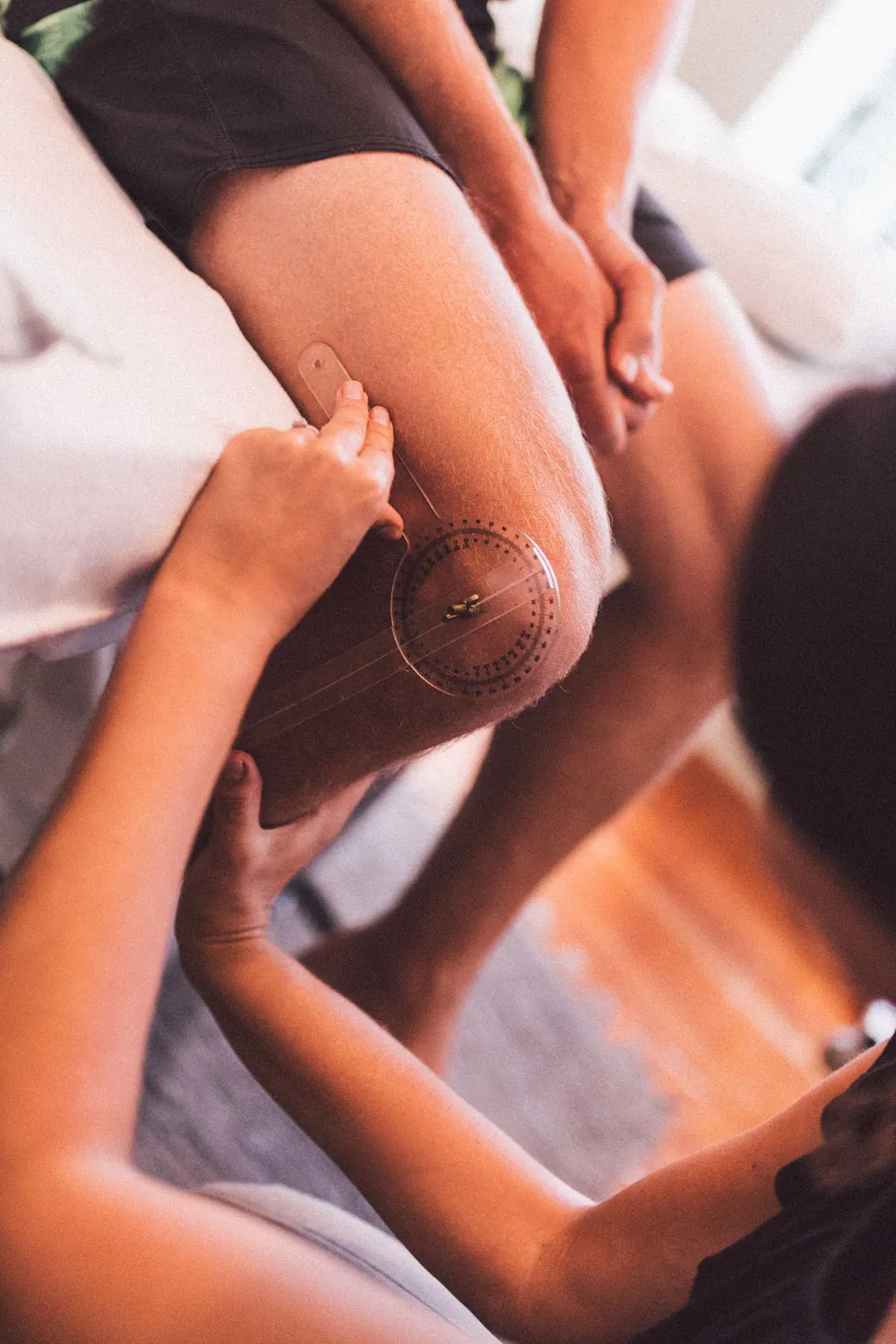
Diagnostic Tests
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a physiotherapist can assess the range of motion, strength, stability, and alignment of the knee joint.
- Imaging: X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound may be recommended to visualise the internal structures of the knee joint, such as bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons
- Special Tests: Various special tests, such as the Lachman test or McMurray test, may be conducted to assess specific structures like the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or meniscus.
Treatment Methods
- RICE Protocol: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation can help alleviate pain and swelling, particularly in the acute phase following an injury
- Exercise Therapy: Physiotherapy exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, improving flexibility, and enhancing proprioception can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future injuries.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage, joint mobilisations, and soft tissue mobilisation can help reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and facilitate tissue healing.
- Bracing or Taping: Depending on the underlying condition, wearing a knee brace or utilising taping techniques may offer support and stability to the knee joint.
- Modalities: Modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or laser therapy may be employed to relieve pain and promote tissue healing.
- Education and Advice: Patients should be educated about proper biomechanics, posture, and activity modification to prevent symptom exacerbation and promote recovery

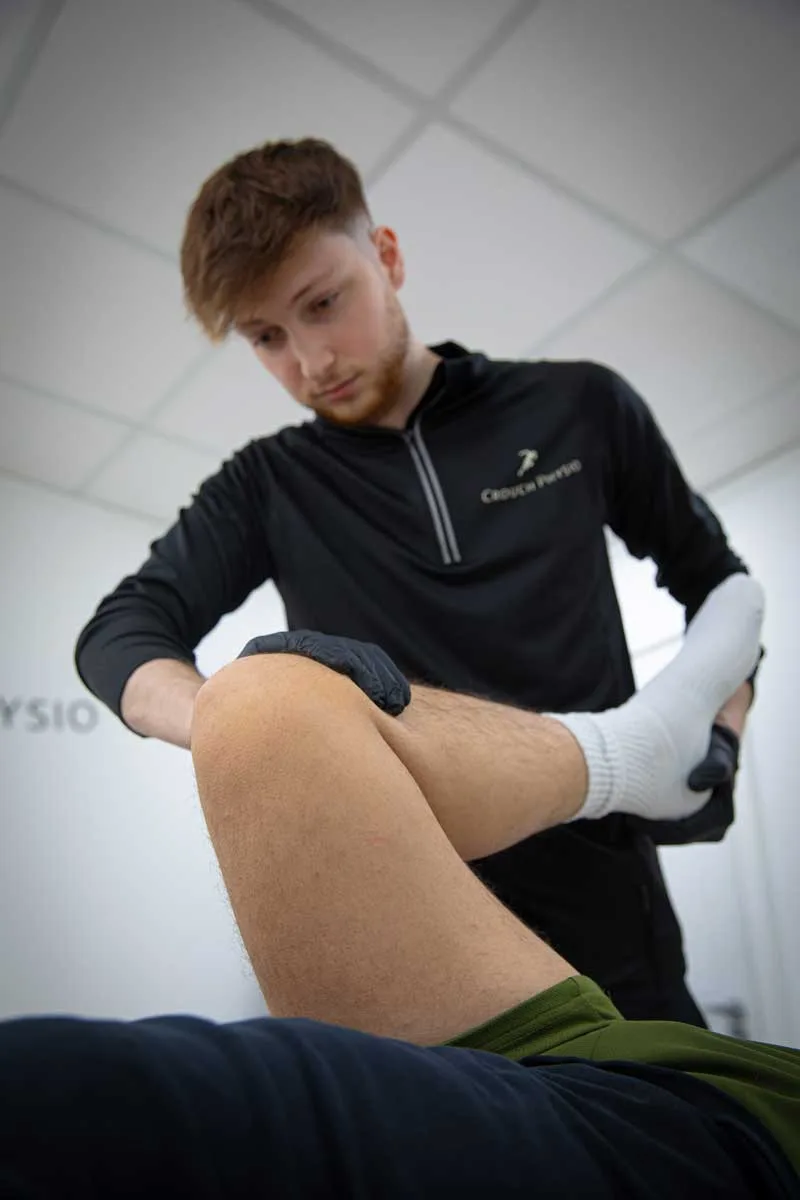
Advice for Patients
- Adhere to the Treatment Plan: Compliance with the prescribed exercise programme and treatment plan is essential for optimal outcomes.
- Manage Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the knee joint and alleviate symptoms.
- Avoid Overuse: Steer clear of activities that worsen symptoms and gradually reintroduce activity under the guidance of a physiotherapist.
- Use Appropriate Footwear: Wearing suitable footwear with good cushioning and support can minimise impact on the knee joint.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to warning signs such as pain or swelling and modify activities accordingly to prevent further injury.




