Osteoporosis
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by weakened bones, making them more prone to fractures. It occurs when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. This imbalance can result in bones becoming fragile and porous over time, leading to increased susceptibility to fractures, especially in areas like the hip, spine, and wrist
Patient Presentation and Symptoms
Patients with osteoporosis may not exhibit noticeable symptoms until they experience a fracture.
However, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Back pain: Often caused by fractures or collapse of vertebrae, resulting in loss of height or curvature of the spine.
- Bone fractures: Fragility fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist, may occur with minimal trauma or even spontaneously.
- Loss of height: Over time, compression fractures in the spine can lead to a gradual loss of height and a stooped posture.
- Bone deformities: Fractures can cause bones to become misshapen or lead to visible spinal curvature (kyphosis).

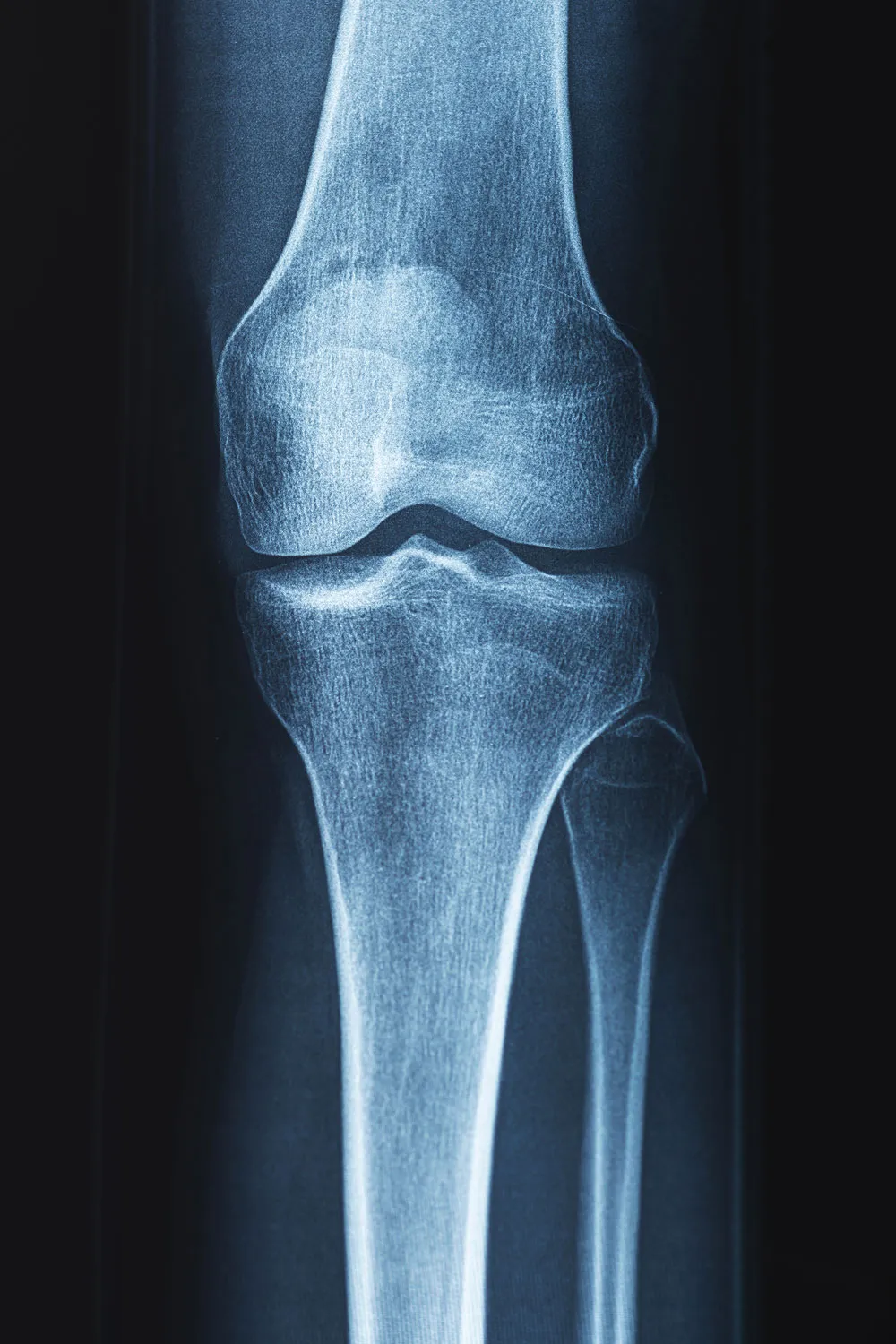
Diagnostic Tests
To diagnose osteoporosis and assess fracture risk, several tests can be performed:
- Bone Density Scan (DEXA scan): This test measures bone mineral density (BMD) and is the most common method for diagnosing osteoporosis.
- X-rays: These can help identify fractures and assess bone quality
- Blood tests: These may be done to check for underlying conditions that could contribute to bone loss
- FRAX score: This tool calculates a person's risk of fracture based on various factors, including age, sex, weight, and bone density.
Treatment Methods
Treatment for osteoporosis typically involves a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes surgical intervention for severe fractures. From a physiotherapist’s perspective, here’s some advice for patients:
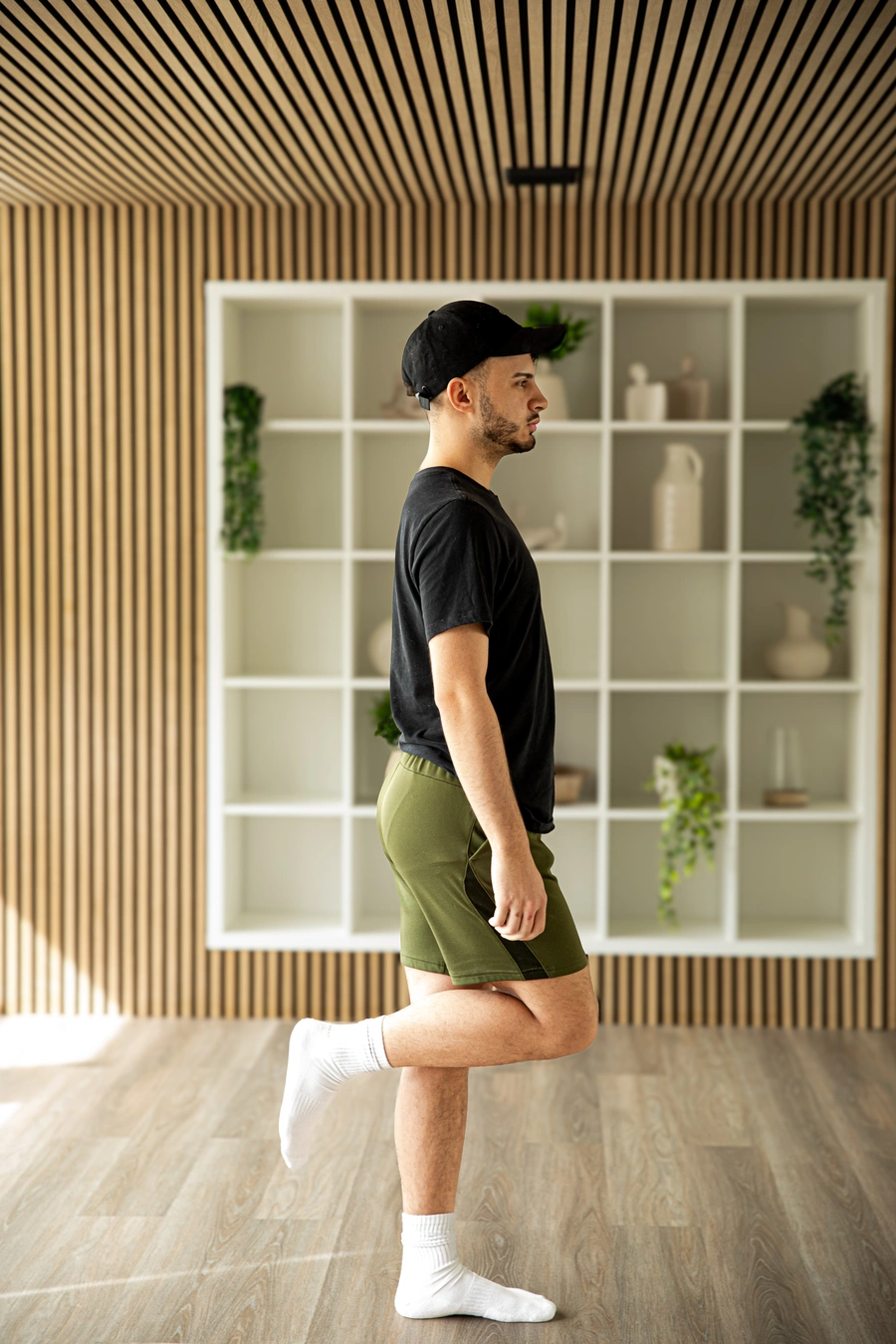
- Weight-bearing exercises: Encourage activities such as walking, jogging, or dancing, which help maintain bone density and strength.
- Resistance training: Incorporate exercises using weights or resistance bands to further strengthen bones and muscles.
- Posture and body mechanics: Educate patients on proper posture and body mechanics to reduce the risk of falls and fractures.
- Balance exercises: Include exercises that improve balance and coordination to help prevent falls.
- Nutrition: Emphasise the importance of a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
- Fall prevention: Assess the home environment for hazards and provide guidance on fall prevention strategies, such as removing tripping hazards and installing grab bars.
- Medication compliance: Encourage patients to adhere to their prescribed medication regimen as directed by their healthcare provider.





